A new flaw in virtual private networks (VPNs) was reported last week at a security conference. The flaw, discovered by a collection of academic and industry researchers, has to do with a vulnerability in how VPN servers assign TCP/IP communication ports and use this to attack their connection tracking feature. This flaw, called port shadowing, is yet another weakness in VPNs that corporate security managers have to worry about.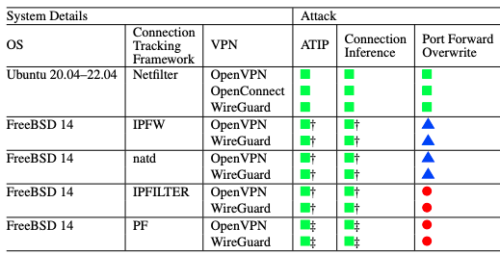 As you can see from the chart below, it goes to the way modern VPNs are designed and depends on Network Address Translation (NAT) and how the VPN software consumes NAT resources to initiate connection requests, allocates IP addresses, and sets up network routes.
As you can see from the chart below, it goes to the way modern VPNs are designed and depends on Network Address Translation (NAT) and how the VPN software consumes NAT resources to initiate connection requests, allocates IP addresses, and sets up network routes.